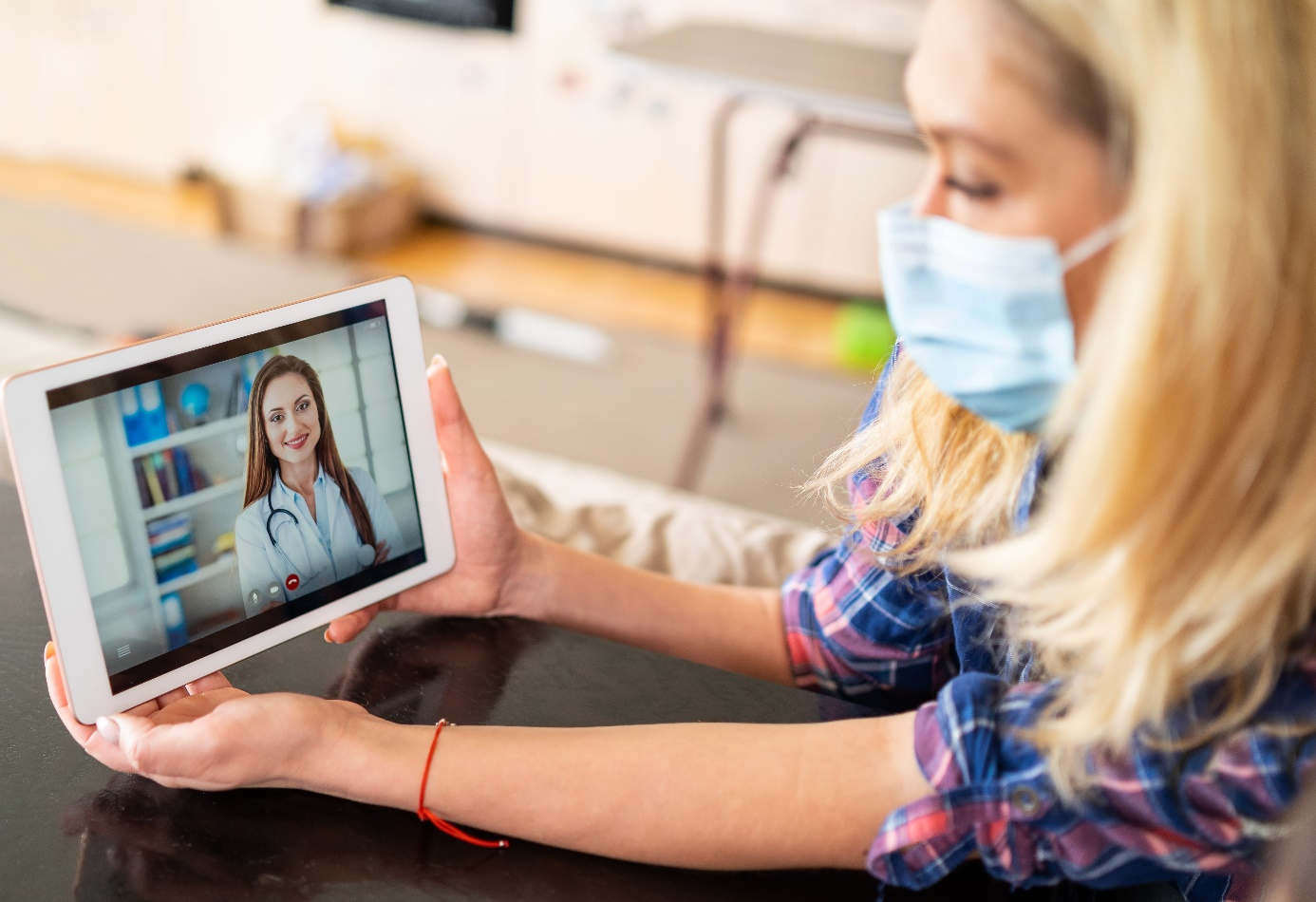
Transforming healthcare with reliable remote solutions via advanced software and secure hardware.
The healthcare industry has seen a rapid shift towards remote work, driven by the need to maintain continuity of care while protecting staff and patients. This transformation requires robust software and hardware solutions tailored to the unique demands of healthcare professionals, ensuring security, efficiency, and seamless communication.
Why Remote Healthcare is Critical Today
The global health landscape, patient expectations, and workforce safety concerns have accelerated the need for remote healthcare solutions. This section explores the driving forces behind this transformation.
Critical Software Tools Powering Remote Healthcare
1. Telemedicine Platforms: Expanding Access Beyond Clinics
Secure, HIPAA-compliant telemedicine platforms allow healthcare providers to offer consultations, diagnosis, and follow-ups remotely, improving accessibility and patient convenience.
2. Electronic Health Records (EHR): Anytime, Anywhere Access
Cloud-based EHR systems ensure that patient data is readily available and updatable from multiple locations, enhancing care coordination and reducing delays.
3. Secure Collaboration Tools: Facilitating Multidisciplinary Care
Encrypted messaging and video conferencing platforms support seamless communication among care teams, fostering collaboration essential for complex case management.
4. Healthcare Analytics: Data-Driven Remote Decision Making
Real-time analytics dashboards provide insights into patient health trends and operational metrics, enabling timely interventions and optimizing resource allocation.

Essential Hardware for Remote Healthcare Delivery
1. Portable Computing Devices: Secure and Flexible Workstations
Laptops and mobile devices equipped with advanced security protocols empower healthcare workers to perform clinical and administrative tasks remotely without compromising data integrity.
2. High-Quality Audio-Visual Equipment: Enabling Clear Telehealth Consultations
Crisp video and audio are vital for effective virtual patient interactions, necessitating reliable cameras and headsets.
3. Secure Network Infrastructure: Protecting Sensitive Information
Robust VPNs, firewalls, and encryption technologies safeguard patient information transmitted over remote networks, ensuring compliance with healthcare data privacy standards.
4. Remote Monitoring Devices: Extending Care Beyond the Facility
Wearable sensors and connected medical devices enable continuous monitoring of patient vitals, allowing clinicians to track health remotely and intervene proactively.

Addressing Security and Compliance in Remote Healthcare
Healthcare organizations must prioritize data security and regulatory compliance when implementing remote work and telehealth solutions. Protecting sensitive patient information is paramount, governed by strict regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the U.S., GDPR in Europe, and others worldwide.
Robust security measures include end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and secure network infrastructure such as VPNs and firewalls to prevent unauthorized access. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments identify and address potential risks proactively. Furthermore, comprehensive staff training on data privacy and cybersecurity best practices helps reduce human errors that could lead to breaches.
Maintaining compliance involves careful vendor selection to ensure third-party software and hardware meet industry standards, as well as clear policies for data handling, access controls, and incident response. By embedding security and compliance at every level, healthcare providers can safeguard patient trust and meet legal obligations while delivering remote care effectively.
The Role of Training and Support in Remote Healthcare Success
Successful implementation of remote healthcare technologies hinges not only on having the right tools but also on ensuring that healthcare professionals are fully equipped to use them effectively. Comprehensive training programs are essential to bridge knowledge gaps and build confidence in adopting new digital workflows. These programs should be tailored to different user roles—from clinicians and nurses to administrative staff—focusing on practical use cases, data privacy, and troubleshooting.

Ongoing technical support is equally critical. Quick access to skilled IT assistance minimizes downtime, resolves technical issues promptly, and maintains uninterrupted patient care. Support teams also help adapt workflows as technology evolves, ensuring staff remain proficient with updates and new features. Ultimately, continuous education and reliable support systems empower healthcare teams to maximize the benefits of remote solutions while maintaining high standards of care.ogy.
Future Trends: What’s Next for Remote Healthcare?
Explore emerging technologies like AI-driven diagnostics, augmented reality for remote surgeries, and blockchain for secure health records management that will shape the future of remote healthcare.
Conclusion
Remote healthcare is no longer optional; it is a critical component of modern medical practice. By investing in cutting-edge software and secure hardware tailored to healthcare’s unique needs, providers can maintain excellence in patient care while enhancing safety and operational efficiency. Collaborations with technology specialists ensure these solutions meet regulatory requirements and adapt to the evolving healthcare landscape.
.